Spring AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming, 관심 지향 프로그래밍)의 개념과 예제에 대한 가이드
1. 개요
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming, 관심 지향 프로그래밍) 는 관심사를 분리하여 모듈성을 높이는 것을 목표로 하는 프로그래밍 패러다임이다. 기존 코드를 수정하지 않고 코드에 작업을 추가하여 동작시킨다. Spring의 AOP 프레임워크를 사용하여 구현해보자.
2. AOP 개념 및 용어
AOP와 관련된 개념과 용어를 살펴보자.
2.1. Business Object
Business Object는 일반적인 비즈니스 로직이 수행되는 일반 클래스이다.
2.2. Aspect
Aspect는 여러 클래스에 적용되는 관심사의 모듈화이다.
통합 로깅은 이러한 cross-cutting concern(교차적 관심)의 예시이다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
class AdderAfterReturnAspect {
private val logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this::class.java)
fun afterReturn(returnValue: Any) {
logger.info("value return was {}", returnValue)
}
}
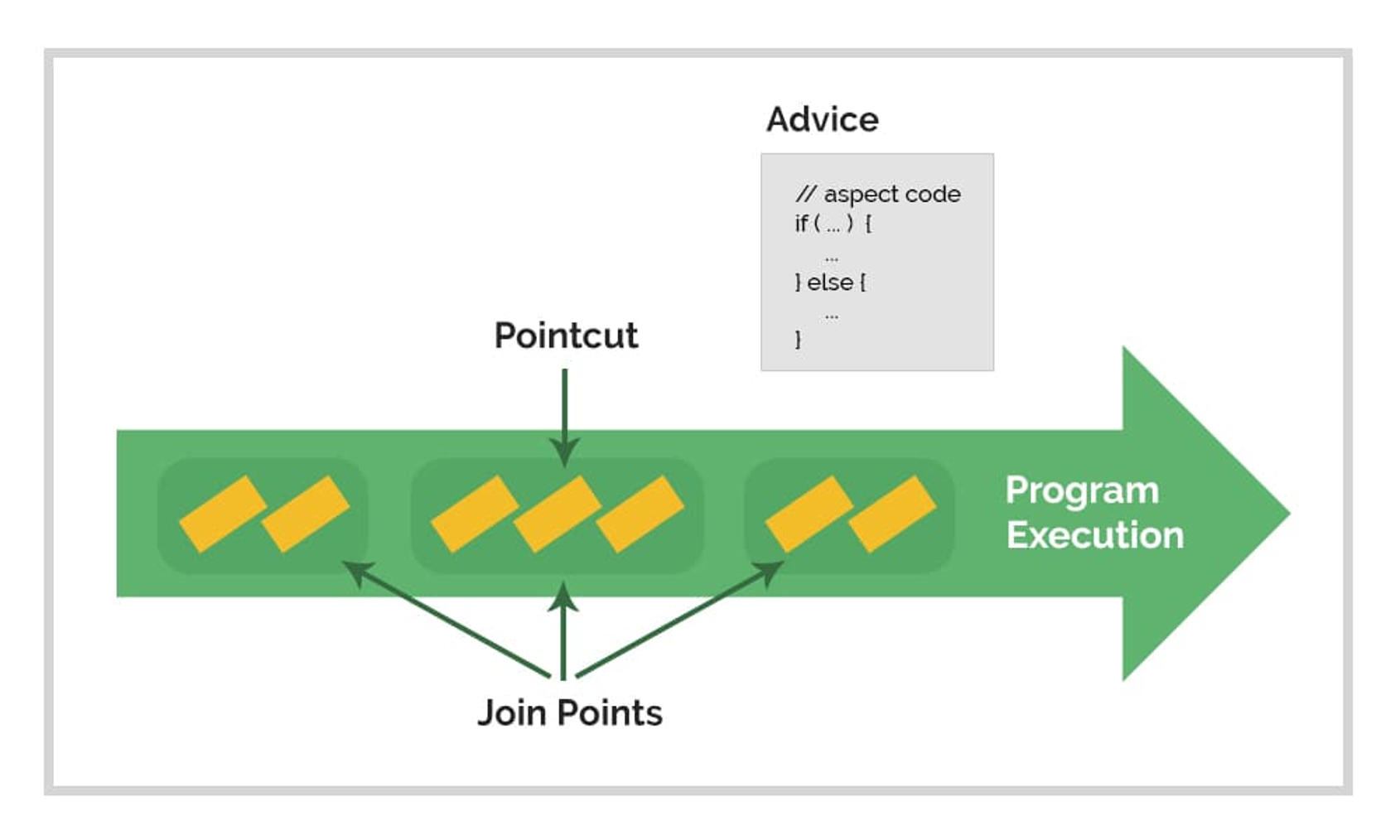
2.3. Joinpoint
Joinpoint 는 메소드 실행이나 예외 처리 등 실행 지점이다.
Spring AOP에서 JoinPoint 는 메소드 실행을 의미한다.
2.4. Pointcut
Pointcut 은 특정 JoinPoint 에서 Aspect 에 의해 적용되는 Advice 를 일치시키는 데 도움이 되는 조건자이다. Spring AOP는 보통 Advice 를 Pointcut 표현식과 연관시키고 Pointcut 과 일치하는 모든 Joinpoint 에서 실행된다.
2.5. Advice
Advice 는 특정 Joinpoint 에서 Aspect가 취하는 조치이다.
Advice 에는 around 와 before , after 유형이 존재한다.
3. AOP 실습
3.1. 의존성 추가
Spring AOP 관련 의존을 추가한다.
1
2
// aop
implementation("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop")
3.2. 사용자 정의 어노테이션 만들기
메소드의 실행 시간을 측정하는 어노테이션을 만들어보자.
1
2
3
@Target(AnnotationTarget.FUNCTION)
@Retention(AnnotationRetention.RUNTIME)
annotation class LogExecutionTime
- @Target : 어노테이션이 적용될 위치를 정의
- @Retention : 어느 시점까지 어노테이션을 유지시킬지 정의
3.3. Aspect 만들기
메소드 실행 시간을 측정할 Aspect를 만들어보자.
1
2
3
4
5
@Aspect
@Component
class ExampleAspect {
}
- @Aspect 어노테이션을 사용하여 Aspect를 정의함
- Spring에서 클래스를 감지하려면 bean으로 등록되어야 하므로 @Component 어노테이션 사용함
3.4. Pointcut과 Advice 만들기
Aspect에 Pointcut과 Advice를 만들어보자.
1
2
3
4
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
fun logExecutionTime(joinPoint: ProceedingJoinPoint): Any? {
return joinPoint.proceed()
}
- @Around 어노테이션을 달아서 메소드 실행 전과 후에 코드 추가를 정의
- @Around 의 포인트컷 인수에는 @LogExecutionTime 어노테이션이 달린 메서드에 적용하라는 조건을 정의
- logExecutionTime() 메소드가 Advice를 의미
- @LogExecutionTime 어노테이션이 달린 메소드가 호출되면, Advice인 logExecutionTime() 메소드가 호출되며 종료된 이후에도 해당 메소드가 호출된다.
3.5. 실행 시간 로깅
Advice에 메소드의 실행 시간을 로깅하는 동작을 추가해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
@Aspect
@Component
class ExampleAspect {
@Around("@annotation(LogExecutionTime)")
fun logExecutionTime(joinPoint: ProceedingJoinPoint): Any? {
val start = System.currentTimeMillis()
val proceed = joinPoint.proceed()
val executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - start
println("${joinPoint.signature} executed in $executionTime ms")
return proceed
}
}
- joinpoint 인스턴스를 사용하기 위해 파라미터로 joinpoint를 정의
- 메서드의 파라미터와 다른 정보에도 접근할 수 있다
다른 클래스에서 메서드를 구현하고 @LogExecutionTime을 달아서 결과를 확인해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
@Component
class BusinessObject {
@LogExecutionTime
fun serve() = runBlocking {
sleep(1000)
}
}
실행할 경우 다음과 같은 결과를 볼 수 있다.
1
void io.tutorial.notificationservice.aop.BusinessObject.serve() executed in 1006 ms
4. 예제 코드
예제 코드는 다음 링크에서 확인할 수 있다.